NVIDIA AI Introduces KVzap: Efficient Cache Pruning
Explore NVIDIA's KVzap, a method for effective cache pruning achieving 2x-4x compression with minimal loss.
The Problem with Current Cache Sizes
As context lengths move into tens and hundreds of thousands of tokens, the key value cache in transformer decoders becomes a primary deployment bottleneck. The cache stores keys and values for every layer and head with shape (2, L, H, T, D). For a vanilla transformer such as Llama1-65B, the cache reaches about 335 GB at 128k tokens in bfloat16, which directly limits batch size and increases time to first token.
Architectural Compression Techniques
Production models already compress the cache along several axes. Grouped Query Attention shares keys and values across multiple queries and yields compression factors of up to 16 across different models. Hybrid models mix attention strategies to reduce the necessity of a full cache.
These methods fail to compress along the sequence axis. Sparse attention retrieves only a subset of the cache, yet all tokens still consume memory. Effective serving of long contexts requires techniques that remove cache entries with minimal impact.
KVpress: An Ecosystem of Pruning Methods
NVIDIA's KVpress project consolidates over twenty pruning techniques into a single codebase. Methods such as H2O, Expected Attention, DuoAttention, and KVzip are benchmarked for their effectiveness.
KVzip and KVzip+: The Scoring Oracle
KVzip stands as the leading baseline for cache pruning. It assigns importance scores to cache entries based on a copy and paste task. Although KVzip+ enhances this scoring by correlating attention weights with actual token contributions, it presents performance challenges during decoding.
Introducing KVzap: A Surrogate Model
KVzap innovates by replacing the scoring system with a surrogate model that analyzes hidden states. It predicts scores for key value heads using an MLP or a simple linear layer, thereby improving computational efficiency.
The training employs a sample of 27k prompts, yielding about 1.2 million training pairs. Across various models, the correlation between predicted and actual scores ranges from 0.63 to 0.77, enhancing predictive accuracy.
Inference Techniques: Thresholding and Sliding Windows
During inference, KVzap prunes low-scoring entries while maintaining a sliding window of the most recent tokens. This approach allows dynamic adaptation to prompt information density, yielding varied compression ratios across different contexts.
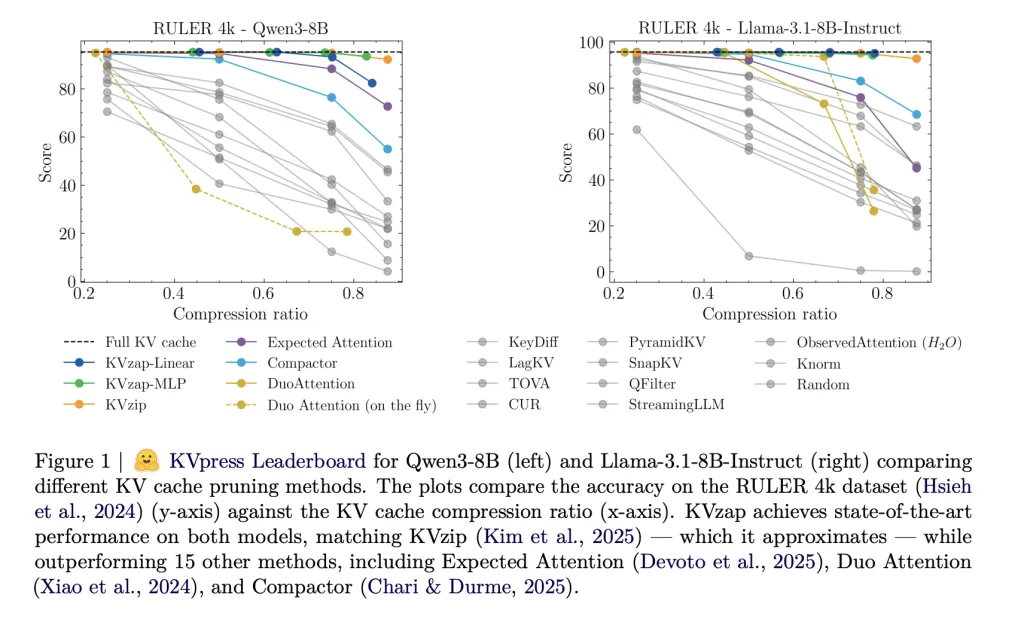
Performance Evaluation on Key Benchmarks
KVzap demonstrates impressive performance on RULER and LongBench benchmarks, achieving significant compression ratios while closely matching the performance of full cache setups. It excels in AIME25 tasks as well, maintaining accuracy even at substantial compression levels.
Key Takeaways
- KVzap substitutes KVzip+ by predicting KV importance scores from hidden states with minimal computational overhead.
- It achieves a squared Pearson correlation ranging around 0.6-0.8, sufficient for effective cache ranking.
- Dynamic adaptation to information density allows varying compression ratios for different prompts.
- Across multiple benchmarks, KVzap achieves notable cache compression while preserving accuracy, showcasing its value in practical applications.
- Open-source implementations in the KVpress framework simplify integration into existing infrastructure.
Сменить язык
Читать эту статью на русском