Introducing Engram: Innovative Memory for Sparse LLMs
DeepSeek introduces Engram, enhancing LLM efficiency with a conditional memory axis.
Understanding the Limitations of Transformers
Transformers rely on attention and Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) for scaling, yet they lack an efficient knowledge lookup mechanism. This leads to repeated computations of the same local patterns, resulting in wasted depth and FLOPs. DeepSeek's Engram module addresses this challenge by implementing a conditional memory axis that complements MoE instead of replacing it.
Engram: A Modern Solution
Engram revitalizes classic N-gram embeddings, offering a scalable O(1) lookup memory that integrates seamlessly into the Transformer backbone. It provides a parametric memory capable of storing static patterns such as common phrases and entities, allowing the main architecture to focus on complex reasoning and long-range interactions.
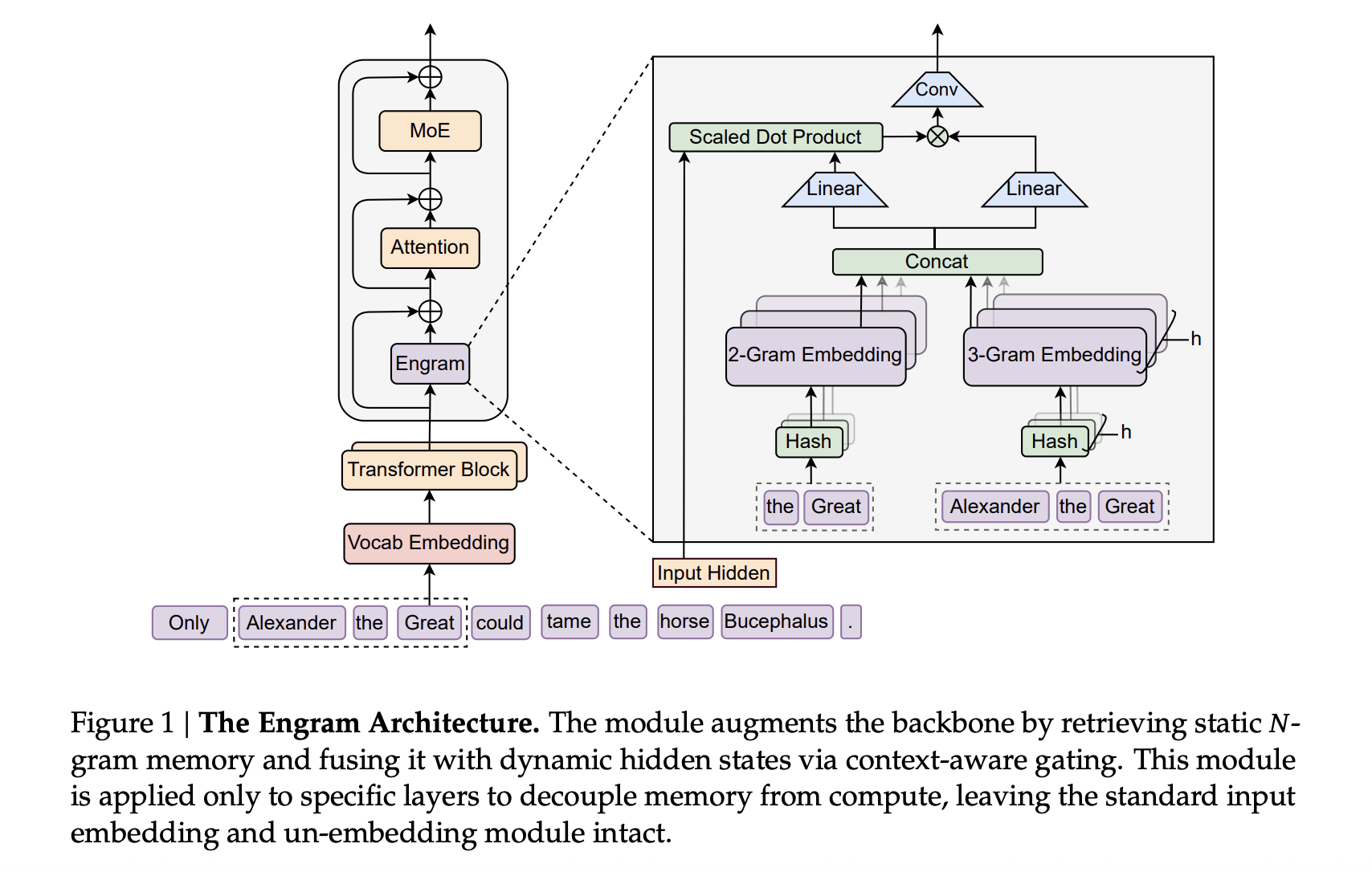
Engram Integration in DeepSeek Transformers
The Engram approach utilizes the DeepSeek V3 tokenizer with a 128k vocabulary, pre-training on 262B tokens. The backbone features a 30-block Transformer with a hidden size of 2560, employing Multi-head Latent Attention with 32 heads, and is optimized using the Muon optimizer.
Engram acts as a sparse embedding module, constructed from hashed N-gram tables. Each N-gram context undergoes a depthwise convolution while a gating mechanism controls the embedding injection. Large-scale models like Engram-27B and Engram-40B share a Transformer backbone with MoE-27B, adjusting parameters to maintain efficiency with reduced routed experts.
Sparsity Allocation: A Fine Balance
The allocation of sparse parameters between routed experts and Engram defines the Sparsity Allocation problem. The research indicates an optimal split between MoE experts and Engram memory to enhance model performance, confirming that these components work best when balanced effectively.
Pre-training Performance Results
Engram-27B and Engram-40B consistently outperformed the MoE-27B baseline across various benchmarks, including language modeling and reasoning tasks. The results show significant reductions in validation loss, indicating the efficiency of the integrating knowledge through Engram.
Long Context Capacity and Performance
Extended context windows of up to 32k tokens were also handled effectively by models leveraging Engram, leading to substantial performance gains in tasks requiring longer context comprehension.
Key Takeaways
- Enhanced Memory Mechanism: Engram introduces an efficient memory system for frequent N-gram patterns to aid dynamic reasoning in LLMs.
- Optimal Resource Allocation: Balancing the sparse capacity between MoE experts and Engram results in improved performance.
- Superior Benchmark Performance: Enhanced capabilities in knowledge and reasoning tasks demonstrate Engram's effectiveness.
- Long Context Improvements: Engram enables higher performance in long-context scenarios without additional computational costs.
For a deeper dive into the research, check out the Engram Paper and explore the GitHub Repo.
Сменить язык
Читать эту статью на русском